소스코드
실습: 비교연산자를 이용한 if 문
if 3 < 5 :
print ("3 < 5가 참이면 이 문장이 표시됨")
if 3 > 5 :
print ("3 > 5가 참이면 이 문장이 표시됨")
if 3 <= 5 :
print ("3 <= 5가 참이면 이 문장이 표시됨")
if 3 >= 5 :
print ("3 >= 5가 참이면 이 문장이 표시됨")
if 3 == 5 :
print ("3 == 5가 참이면 이 문장이 표시됨")
if 3 != 5 :
print ("3 != 5가 참이면 이 문장이 표시됨")
에어컨 온도조절 동작 코드
temp = 33
user_want_temp = 26
if temp <= user_want_temp :
print("에어컨을 잠시 멈춥니다.")
수박이 20,000원 미만이면 한 통 사와
water_melon = 25000
if water_melon < 20000 :
print("수박을 한 통 구입합니다")
온도가 내려가 에어컨이 멈추면 다시는 에어컨이 재가동되지 않는 문제 해결
temp = 27
user_want_temp = 26
if temp <= user_want_temp :
print("에어컨을 잠시 멈춥니다.")
else :
print("에어컨을 가동합니다.")
수박이 20,000원 미만이면 2통 사오고, 그 이상이면 1통만 사와
water_melon = 19000
if water_melon < 20000 :
print("수박을 2통 구입합니다.")
else :
print("수박을 1통 구입합니다.")
수박이 20,000원 미만이고 사이다가 1,000원 미만이면 둘 다 하나씩 사와. 그렇지 않으면 아무 것도 사오지 마.
water_melon = 19000
cider = 950
if water_melon < 20000 :
if cider < 1000 :
print("수박 1통과 사이다 1개를 구입합니다.")
수박이 20,000원 미만이고 사이다가 1,000원 미만이면 둘 다 하나씩 사와. 그렇지 않으면 아무 것도 사오지 마.
water_melon = 19000
cider = 1000
if water_melon < 20000 :
if cider < 1000 :
print("수박 1통과 사이다 1개를 구입합니다.")
else:
print("수박은 싼 데 사이다가 비싸서 아무 것도 안 사감")
else:
print("일단 수박부터 비싸서 아무 것도 안 사감")
수박이 20,000원 미만이면 3통 사오고, 20,000원 이상 ~ 25,00미만이면 2통만 사오고, 25,000원 이상이면 1통만 사와
if water_melon < 20000 :
print("수박을 3통 구입합니다.")
else :
if water_melon < 25000 :
print("수박을 2통 구입합니다.")
else :
print("수박을 1통 구입합니다.")
수박이 20,000원 미만이면 3통 사오고, 20,000원 이상 ~ 25,00미만이면 2통만 사오고, 25,000원 이상이면 1통만 사와
if water_melon < 20000 :
print("수박을 3통 구입합니다.")
elif water_melon < 25000 :
print("수박을 2통 구입합니다.")
else :
print("수박을 1통 구입합니다.")
실습: 약속에 늦은 날(elif)
message = "" # 메시지
late = 20 # 지각할 거 같은 시간(분)
if late < 5 :
message = ""
elif late < 20 :
message = "미안하다"
else:
message = "오늘 자동차가 펑크날거 같아"
if message != "":
print("친구에게 다음과 같이 메시지를 보냈습니다: ", message)
반복문 - while
a = 0
while a < 3 :
print (a)
a = a + 1
반복문 - while
a = 0
while True :
print (a)
a = a + 1
1, 3, 5, 7, 9, … 와 같이 홀수만 99까지 출력
a = 1
while a <= 99 :
print(a)
a = a + 2
반복문 - for
data = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
for a in data :
print (a)
1-9까지의 숫자를 list로 만들고 그 목록을 하나씩 출력
nums = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9]
for a in nums :
print (a)
좋아하는 음식을 list로 만들고 그 목록을 하나씩 출력
food_list = ["짜장", "회", "탕수육", "트러플버섯", "치킨"]
for food in food_list :
print (food)
좋아하는 음식을 list로 만들고 그 목록 중 “치킨“이 있을 때만 “치킨 찾았다!” 출력
food_list = ["짜장", "회", "탕수육", "트러플버섯", "치킨"]
for food in food_list :
if food == "치킨" :
print (food, "찾았다!")
좋아하는 음식을 list로 만들고 그 목록 중 “탕수육“이 있을 때만 “탕수육 찾았다! O번째에 있었어!” 출력
food_list = ["짜장", "회", "탕수육", "트러플버섯", "치킨"]
index = 0
for food in food_list :
if food == "탕수육" :
print (food, "찾았다!", index, "번째에 있었어!")
index = index + 1
무의미한 반복 작업 중단 - break
food_list = ["짜장", "회", "탕수육", "트러플버섯", "치킨"]
index = 0
for food in food_list :
if food == "탕수육" :
print (food, "찾았다!", index, "번째에 있었어!")
break;
index = index + 1
break 문이 없을 때
food_list = ["짜장", "회", "탕수육", "트러플버섯", "치킨"]
index = 0
for food in food_list :
print(index, "번째 자료 조사 중...")
if food == "탕수육" :
print (food, "찾았다!", index, "번째에 있었어!")
index = index + 1
break 문이 있을 때
food_list = ["짜장", "회", "탕수육", "트러플버섯", "치킨"]
index = 0
for food in food_list :
print(index, "번째 자료 조사 중...")
if food == "탕수육" :
print (food, "찾았다!", index, "번째에 있었어!")
break;
index = index + 1
목록 중 ‘트러플버섯’ 사달라고 조를 때
food_list = ["짜장", "회", "탕수육", "트러플버섯", "치킨"]
for food in food_list :
if food != "트러플버섯" :
continue
print (food, "사 주세요!")
반복문으로 list 값 추가하기(list comprehension)
for i in range(5):
print(i)
range() 함수 사용해 list 값 추가
a = [i for i in range(10)]
range() 함수 사용해 list 값 추가
a = [i*2 for i in range(10)]
함수 사용하기
def plus1(a) :
b = a + 1
plus1(10)
함수 결과를 사용하자 - return
def plus1(a) :
b = a + 1
return b
c = plus1(10)
print(c)
실습: 두 수를 더해서 return 하는 함수
def plus_2(a, b) :
return a + b
a = plus_2(10, 20)
print(a)
실습: 두 수를 빼서 return 하는 함수
def minus_2(a, b) :
return a - b
a = minus_2(10, 20)
print(a)
실습: 두 수 중 더 큰 수를 return 하는 함수
def get_max(a, b):
if a < b :
return b
else :
return a
res = get_max(10, 11)
print(res)
실습: 두 수 중 더 작은 수를 return 하는 함수
def get_min(a, b):
if a < b :
return a
else :
return b
res = get_min(10, 11)
print(res)
파이썬의 정규표현식
import re
pattern = re.compile('연어')
pic = '멸치요리.jpg'
m = pattern.search(pic)
파이썬의 정규표현식
import re
pattern = re.compile('멸치')
pic = '멸치요리.jpg'
m = pattern.search(pic)
파일명으로 리스트 만들고, 그 리스트를 돌며 ’연어’라는 글자가 들어있는 파일명만 찾기
import re
files = ["멸치요리.jpg", "연어요리.jpg", "연어 튀기기 전.png"]
pattern = re.compile('연어')
for item in files:
m = pattern.search(item)
if m != None:
print(item, '은 조건에 맞음.')
else:
print(item, '은 조건에 맞지 않음')
시작이 같은지 검사하기 : K로 시작하는지 검사
import re
pic = "Korea.jpg"
pattern = re.compile('^K')
m = pattern.search(pic)
import re
pic = "booK.jpg"
pattern = re.compile('^K')
m = pattern.search(pic)
끝이 같은지 검사하기: ’jpg’로 끝나는지 검사하기
import re
pic = "booK.jpg"
pattern = re.compile('jpg$')
m = pattern.search(pic)
import re
pic = "booK.jpg"
pattern = re.compile('png$')
m = pattern.search(pic)
input() 함수 사용
a = input()
print(a)
화면에 메시지 출력하면서 입력하라고 안내
a = input(“입력하세요:”)
print(a)
input() 함수 사용
a = int( input("1~3중 입력하세요: ") )
print(a)
사용자 키보드로 숫자 값을 받아 1 더한 값을 보여주는 프로그램
a = int( input("숫자를 입력하세요: ") )
b = a + 1
print("결과 :" , b)
사용자 키보드로 숫자 값을 받아 1 뺀 값을 보여주는 프로그램
a = int( input("숫자를 입력하세요: ") )
b = a - 1
print("결과 :" , b)
사용자 키보드로 이름 받아 뒤에 “님 안녕하세요”를 보여주는 프로그램
a = input("이름을 입력하세요: ")
b = a + "님 안녕하세요"
print("결과 : " , b)
파일 새로 만들고 파일에 내용 쓰기
# 파일 생성하고 열기
file = open("sample.txt", 'w')
# 파일에 내용 쓰기
file.write("안녕하세요")
# 파일 닫기. 파일을 열었으면 꼭 닫아야 한다
file.close()
파일 읽기
# 파일 생성하고 열기
file = open("sample.txt", 'r')
# 파일 내용에서 맨 위 한 줄 읽어 오기
line = file.readline()
print (line)
# 파일 닫기. 파일을 열었으면 꼭 닫아야 한다
file.close()
반복문으로 여러 줄 쓰기
file = open("여러줄.txt", 'w')
index = 1
while index <= 100 :
file.write(str(index))
file.write("\n")
index = index + 1
file.close()
여러 줄 읽기
file = open("여러줄.txt", 'r')
while True:
line = file.readline()
if not line:
break;
print (line)
file.close()
여러 줄 읽기
file = open("여러줄.txt", 'r')
all_line_list = file.readlines()
for line in all_line_list :
print(line)
file.close()
sample.csv
file = open("sample.csv", 'w')
file.write ("이름,전화번호\n")
file.write ("홍길동,02-1111-1111\n")
file.write ("박길동,02-1111-2222\n")
file.write ("최길동,03-1111-3333\n")
file.close()
math
import math
# 올림. 주어진 수보다 큰 수중 가장 작은 정수
a = math.ceil(3.1)
# 내림. 주어진 수보다 작은 수중 가장 큰 정수
b = math.floor(3.1)
# 최대공약수
c = math.gcd(12, 20, 40, 60)
print(a, b, c)
random
import random
# 1~10 사이 아무 정수나 생성
a = random.randint(1,10)
# 0 <= x < 1 사이의 실수 생성
b = random.random()
print(a, b)
matplotlib
import matplotlib.pyplot
matplotlib.pyplot.plot([1, 5, 3, 3, 4])
matplotlib.pyplot.show()
matplotlib
import matplotlib.pyplot
matplotlib.pyplot.plot([1, 5, 3, 3, 4], 'ro')
matplotlib.pyplot.show()
pandas
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame(columns = ['이름','키'])
df['이름'] = ["홍길동", "박길동", "김길동"]
df['키'] = [175, 183, 178]
print(df)
pandas 엑셀 파일로 저장하기
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame(columns = ['이름','키'])
df['이름'] = ["홍길동", "박길동", "김길동"]
df['키'] = [175, 183, 178]
print(df)
df.to_excel('test.xlsx')
pandas 자료를 matplotlib 로 시각화
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
df = pd.DataFrame(columns = ['이름','키'])
df['이름'] = ["홍길동", "박길동", "김길동"]
df['키'] = [175, 183, 178]
df.plot()
plt.show()
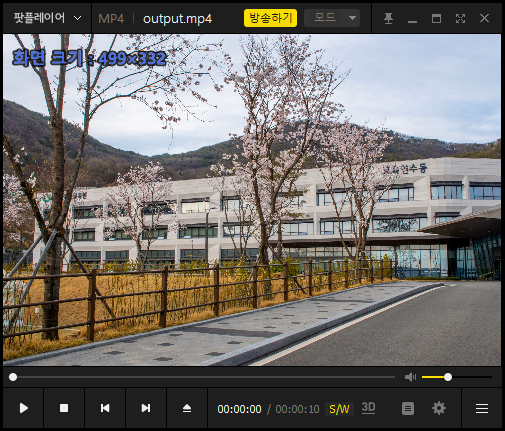
moviepy
from moviepy.editor import ImageSequenceClip
# 이미지 파일이 저장된 폴더 경로
image_folder = 'images'
video_name = 'output.mp4'
# 이미지 시퀀스 클립 생성 (fps: 초당 프레임 수)
clip = ImageSequenceClip(image_folder, fps=1)
# 비디오 저장
clip.write_videofile(video_name)
결과